 You’ve probably heard about fiber optics from something like a phone carrier television advertisement, but what exactly are fiber optic cables and what are the benefits?
You’ve probably heard about fiber optics from something like a phone carrier television advertisement, but what exactly are fiber optic cables and what are the benefits?
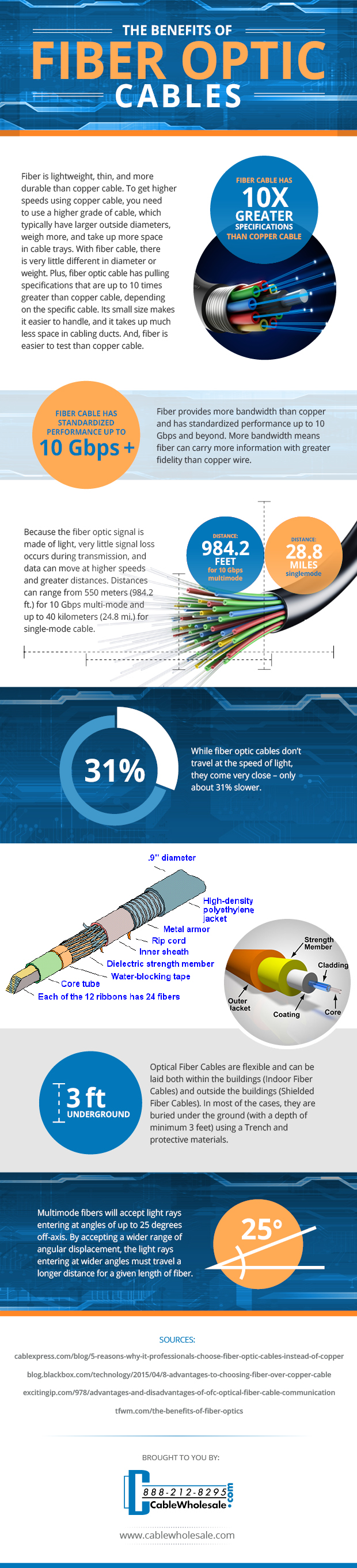
For starters, they’re fast. Very fast. Not quite as fast as the speed of light, but only about 31% slower. The secret behind fiber optic cables lies in the fiber itself. Compared to the traditional copper most cables use, fiber provides more bandwidth and has standardized performance up to 10 Gbps and beyond. Greater bandwidth capabilities means these cables can carry more information (data) with even more reliable integrity than copper wire.
Another benefit of fiber optic cables is that very little signal loss occurs during transmission, because the fiber optic signal is made of light. This allows data to move at higher speeds and for greater distances. As far as 550 meters (984.2 ft.) for 10-Gbps multimode and up to 40 kilometers (24.8 mi.) for single-mode cable.
On a practical level, fiber is lightweight, thin, and more durable than copper wire. You must use a higher grade of cable – which typically have larger outside diameters, weigh more, and take up more space in cable trays – in order to get higher speeds with copper cable.
Fiber cables, on the other hand, have very little differences in diameter or weight. In addition, fiber optic cable has pulling specifications that are up to 10 times greater than some copper cables. The smaller size makes storing, using, and overall management of fiber much easier to handle than copper cable. Plus, it’s easier to test fiber.
Optical Fiber Cables are flexible and versatile. They can be laid either outside of buildings (Shielded Fiber Cables) or inside (Indoor Fiber Cables). Typically, they are buried a minimum of three feet underground using a trench and protective materials.
Finally, there are also what’s known as multimode fibers. These will accept light rays entering at angles of up to 25 degrees off-axis. By accepting a wider range of angular displacement, the light rays entering at wider angles must travel a longer distance for a given length of fiber.



